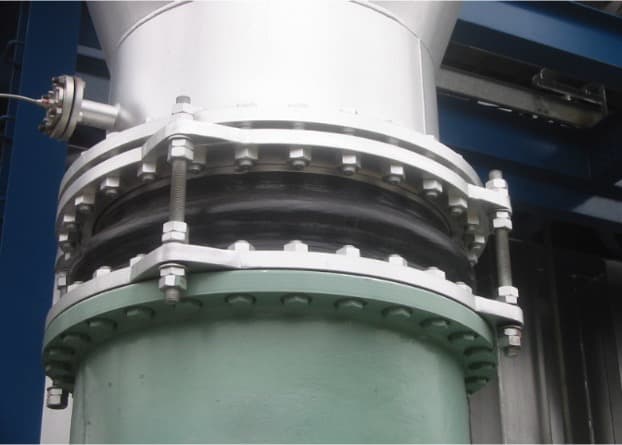

Rubber Expansion Joint
Expansion joint solves a piping system problem
Proper Application
- Expansion joint is used in the middle of pipe to absorb extension and compression at pipe line due to vibration, noise and temperature change.
- For both delivery and suction
Characteristics
Quick Shape Recovery to the Original Form
Arch structure for flexible part of the body absorbs various kinds of defomation brought by external force.
Easy Installation
Light weight and easy to handle.
Wrapped type. One size fits all.
Face-to-face length can be designed depend on install situation.
Kinds
Metal Flange Type
2 Types; A type (for dredging & heavy purpose) and B type (for general purpose)
Suitable for less than 0.98MPa at working pressure.
Loose end type is also avavailable depending on difficulty of installation of pipes.
Easy to install owing to built-in control unit.
Metal Flange - A Type
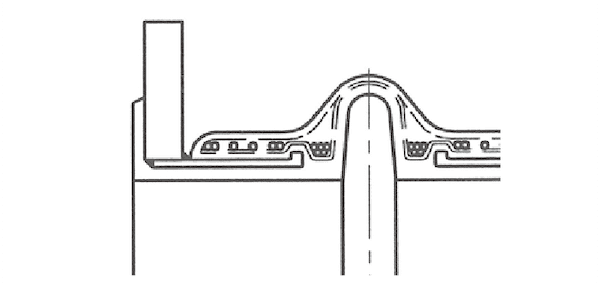
Metal Flange - B Type
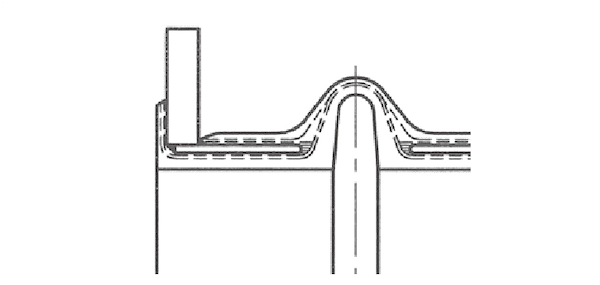
Rubber Flange Type
Suitable for less than 0.49MPa at working pressure.
Face-to-face distance is short and very light weight.
Retaining ring is adhered by vulcanizing.
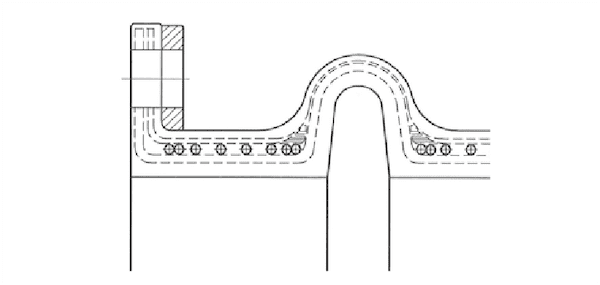
Structure
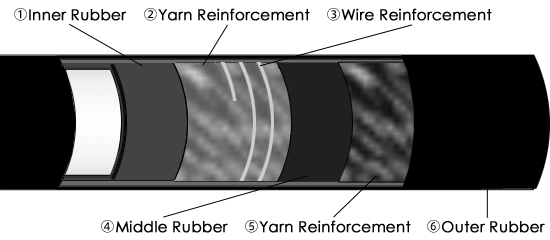
The picture above is very simple.
Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Standard Specification
| ND | in. | ID mm |
Standard Length | Working Pressure | Tolerable Movement | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Arch mm |
2 Arches mm |
Low Pressure MPa |
High Pressure MPa |
Compression mm |
Extension mm |
Deflection mm |
|||
| 40 | 1-1/2 | 38.1 | 130 | 200 | 0.49 | 0.98 | 9 | 5 | 5 |
| 50 | 2 | 50.8 | 12 | 7 | 7 | ||||
| 65 | 2-1/2 | 63.5 | |||||||
| 80 | 3 | 76.2 | 210 | ||||||
| 100 | 4 | 101.6 | |||||||
| 125 | 5 | 127.0 | 150 | 240 | 15 | 8 | 8 | ||
| 150 | 6 | 152.4 | |||||||
| 200 | 8 | 203.2 | 180 | 290 | 18 | 10 | 10 | ||
| 250 | 10 | 254.0 | 200 | 310 | |||||
| 300 | 12 | 304.8 | 230 | 340 | |||||
| 350 | 14 | 330.2 | 350 | 0.78 | 21 | 12 | 12 | ||
| 400 | 16 | 381.0 | 360 | ||||||
| 450 | 18 | 432.0 | 240 | 370 | |||||
| 500 | 20 | 489.0 | 250 | 380 | 0.29 | 24 | 13 | 15 | |
| 550 | 22 | 534.0 | |||||||
| 600 | 24 | 591.0 | 400 | ||||||
| 650 | 26 | 638.0 | 0.59 | ||||||
| 700 | 28 | 698.0 | |||||||
| 750 | 30 | 738.0 | 260 | ||||||
| 800 | 32 | 791.0 | |||||||
| 900 | 36 | 898.0 | |||||||
| 1000 | 40 | 998.0 | 300 | 480 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 30 | 16 | |
| 1100 | 44 | 1100.0 | 500 | ||||||
| 1200 | 48 | 1200.0 | |||||||
| 1350 | 54 | 1350.0 | 350 | 570 | 36 | 20 | 20 | ||
| 1500 | 60 | 1504.0 | |||||||
Tolerable movement data shown are based on 1 arch.
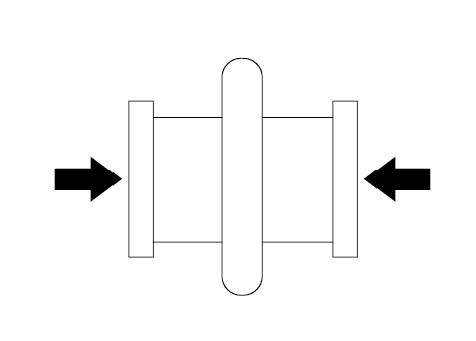
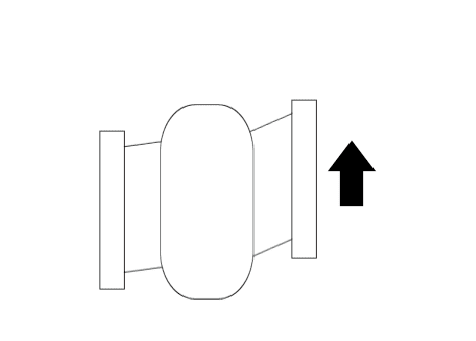
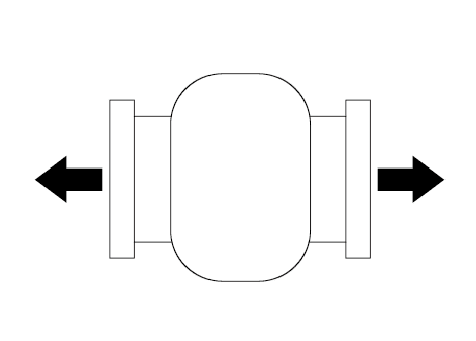
Movement
Axial Compression
Deflection
Axial Extention
All Products
-
Rubber & Flake Lining
-
Rubber Hose
-
Rubber & Plastic Extrusion
-
Rubber Molding







